
Home > Support > Technical Info > 5 Common Solenoid Valve Malfunctions
5 Common Solenoid Valve Malfunctions
and How to Fix Them
Solenoid valves are widely used in various automated control systems, including fire protection systems, water treatment equipment, steam pipelines and other fluid control scenarios. Although they have a simple structure and compact size, improper installation, impurities in the fluid, or operating conditions that do not meet product specifications may cause the solenoid valve to fail to open or close normally, leak, overheat the coil and other common faults, thereby affecting the overall system's operating efficiency and safety. For these common problems, maintenance measures usually include removing internal impurities, replacing damaged parts, adjusting the inlet and outlet pressure difference, or optimizing the power supply and heat dissipation design. This article will systematically organize the failure phenomena, potential causes and corresponding troubleshooting methods of solenoid valves to assist engineers in quickly locating problems and restoring normal equipment operation.
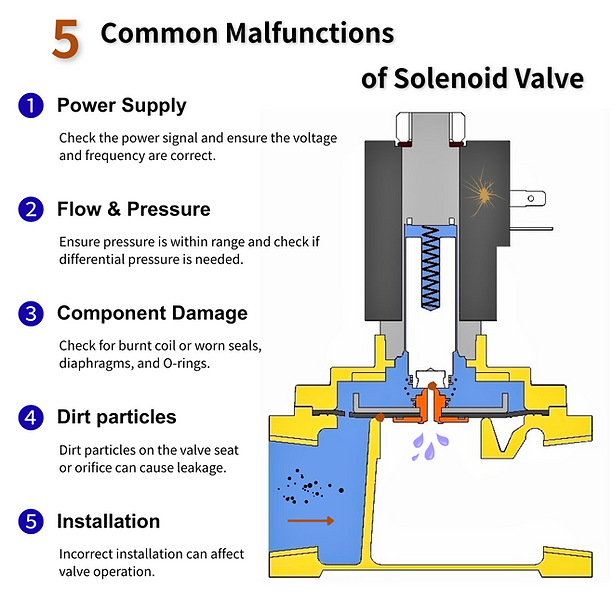
Common solenoid valve failure problems
Solenoid valves play a vital role in automation systems, primarily responsible for opening and closing fluids. However, over time, solenoid valves often malfunction, which not only affects equipment operation but can also lead to higher repair costs and reduced production efficiency.
KUHNWAY has over 30 years of experience in solenoid valve design and sales. While assisting customers, we frequently encounter solenoid valve malfunctions. To help field engineers quickly identify problems, we've compiled several of the most common malfunction symptoms and troubleshooting methods. Through basic observation and simple testing, engineers can effectively identify the root cause of the problem and recommend appropriate solutions to restore equipment to normal operation.
-
Solenoid valve does not open
Failure to open or incomplete opening of a solenoid valve is one of the most common faults. This typically results in fluid flow being blocked, leading to abnormal system pressure. In many industries, such as manufacturing and the chemical industry, this type of failure can cause production halts or material loss. The most common causes include power problems, insufficient fluid pressure, coil failure, and obstruction of the valve body.
Incomplete opening of a solenoid valve can cause unstable flow and disrupt proper fluid distribution. When troubleshooting, first check the power supply and control signal, then confirm the presence of foreign matter in the valve body, and finally test the coil.
-
Solenoid valve does not close
Another critical issue is solenoid valve failure to close or incomplete closing, often leading to liquid or gas leakage, which not only damages equipment but can also pollute the environment. This issue can pose a safety hazard in many high-temperature, high-pressure systems or those handling corrosive fluids. Such failures may stem from factors such as valve body aging, worn seals, or valve seat sticking due to fluid impurities.
In steam supply systems, if a solenoid valve fails to close completely, it will cause continuous steam leakage, further reducing system energy efficiency, increasing energy costs, and even impacting the normal operation of other equipment. To troubleshoot this issue, first inspect the valve body and surrounding area for signs of steam leakage. Then, clean the valve interior to remove any impurities or deposits. If necessary, replace any damaged sealing elements or valve body components to restore the valve's proper closing function.
-
Solenoid valve coil issue
Coil burnout or melting is a serious and destructive problem in solenoid valve failures. When the solenoid valve coil overheats, it can cause the device to fail to start properly or operate erratically. This condition is often caused by prolonged power-on, unstable voltage, or high-frequency operation. Physical damage to the coil or internal short circuits are also common causes of failure.
Visual inspection is a preliminary and effective method for detecting coil failures. Check the coil for visible deformation, burn marks, or abnormal color. Additionally, smell a burning odor, which is often a sign of coil overheating or burnout. If the solenoid valve is completely unresponsive after powering on, check the power supply and control system to confirm that the signal is properly transmitted to the coil.
If these inspections fail to locate the fault, disassemble the coil and conduct a detailed inspection. Use a multimeter to measure the coil's resistance to verify that it is within the normal range. If the result indicates a short or open circuit, replace the coil immediately.
-
Solenoid valve noise problem
A solenoid valve should emit a subtle operating sound during normal operation, but any abnormal noise is often a precursor to a malfunction. Common noise issues include humming, vibration, and knocking sounds caused by fluid impact. These abnormal sounds not only affect the normal operation of the equipment but can also disrupt the surrounding working environment.
Common causes of noise include wear of internal valve components, blockage by foreign matter, and excessive fluid flow. For example, in an automated production line, if a solenoid valve opens and closes rapidly, it will generate severe noise, potentially damaging other equipment and causing discomfort to operators. To address noise issues, engineers can first conduct a full system inspection to ensure that all components are functioning properly, and then perform targeted maintenance or replace any problematic parts.
Analysis of solenoid valve failure causes
-
Power supply
Power supply problem is one of the important reasons for solenoid valve failure. If the solenoid valve fails to operate normally, you need to check the power supply first.
-
Power not supplied
If power is not supplied, the solenoid valve will not function properly. This is often caused by a power line fault or improper switch operation. Check that the power connection is intact, the power switch is turned on, and there are no unexpected power outages. Depending on the machine's operating environment, prolonged exposure to moisture in the power outlet can cause poor contact. Therefore, be sure to measure the voltage during inspection to confirm that the power supply to the solenoid valve is normal.
-
Voltage or frequency incorrect
Many solenoid valves require specific operating voltages and frequencies. Voltages that are too high or too low can impair proper operation. For example, with a common 220V AC voltage, voltages below 150V or above 300V can cause the solenoid valve to malfunction or even burn out the coil. Measuring the voltage and frequency of your application to ensure they are within the specified range can reduce the chance of malfunction.
-
Fluid pressure problems
Fluctuations in fluid pressure directly affect the performance of solenoid valves when controlling fluids. Excessively high or low fluid pressure can cause the solenoid valve to malfunction.
-
Pressure difference is too high or too low
When designing a solenoid valve, an optimal operating pressure range is often set. Fluid pressure differences exceeding the design specifications can cause the valve to stick or malfunction. If the inlet fluid pressure exceeds the valve's tolerance, it can easily cause valve body deformation or seal loss. Conversely, if the pressure is too low, the valve may not open, preventing the upstream fluid from flowing smoothly.
-
Pressure pulse or back pressure generated upstream
In some cases, pressure pulses or backpressure generated by upstream equipment can affect the operation of solenoid valves. This is especially true in production systems, where drastic changes in fluid flow rate can cause momentary pressure fluctuations. Therefore, it's recommended to incorporate pressure reducing valves and buffers into piping system designs to stabilize fluid flow and prevent valve failures caused by pressure fluctuations.
-
Solenoid valve parts are damaged
The mechanical parts of the solenoid valve often suffer various damages due to long-term operation or external environmental influences, which will have a serious impact on its performance.
-
Coil burnt out
The coil, a core component of a solenoid valve, can overheat and burn out if energized for extended periods, preventing the valve from starting or operating. When the current exceeds the designed load, heat buildup can accelerate the degradation of the coil's insulation, leading to a short circuit. Therefore, installing an overload protection device is recommended to prevent this problem.
-
Valve body damaged or deformed
Prolonged fluid erosion and vibration can cause deformation or damage to the solenoid valve body, affecting its sealing performance and opening efficiency. Valves made of substandard manufacturing and materials are particularly prone to such problems. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn parts are key to maintaining normal operation.
-
Corrosion Issues
Corrosive media in the fluid can gradually erode the metal components of the solenoid valve. When working with acidic, alkaline, or other chemically charged fluids, the solenoid valve should be constructed of suitable materials to prevent valve failure due to corrosion. According to industry standards, valves should be regularly inspected for signs of corrosion and promptly addressed.
-
Bent or Damaged Ferromagnetic Tubes
Ferromagnetic tubes play a critical role in the operation of the solenoid valve. If deformed or damaged due to external forces or aging, the solenoid valve's switching function will be directly affected. Regularly inspect the condition of the ferromagnetic tubes to prevent them from affecting the valve's proper operation.
-
Dirt particles in the fluid
Leaks in the solenoid valve can occur due to tiny particles such as swarf, rust, and sand adhering to the valve seat or orifice. Even very small particles can cause problems. Carefully clean the valve components and ensure that the piping is clean. Install a filter if necessary.
-
Dirt or Damage on the Diaphragm
If dirt accumulates or is damaged on the solenoid valve diaphragm, it can cause flow restriction or air leakage, and even lead to valve failure. To address this issue, strengthen fluid filtration measures and regularly clean and inspect the diaphragm to ensure proper operation.
-
Foreign Objects on the Valve Seat or Pipeline
If the valve seat and connected piping are clogged with foreign objects, fluid flow will be blocked, causing the valve to malfunction. Therefore, when designing the piping system, consider installing filters to prevent foreign objects from entering the solenoid valve. During each maintenance session, check the seal of the valve seat and the cleanliness of the piping.
-
Blockage of the Pilot Hole
Blockage of the pilot hole can affect the start and return speed of the solenoid valve, especially in applications with high speed requirements. Checking the pilot hole for unobstructed flow and regularly cleaning it can help improve the efficiency of the solenoid valve.
-
Installation Issues
Improper installation can also degrade the performance of the solenoid valve and even affect the operation of the entire system.
-
Missing Parts After Repair
When repairing or replacing a solenoid valve, improper installation of the relevant parts may cause the valve to malfunction. Therefore, a detailed inspection is required after repair to ensure that all parts are fully installed and functioning properly.
-
Incorrect Installation Orientation
Incorrect installation orientation of the solenoid valve will directly affect the flow direction and the valve's switching performance. Installation should be performed strictly in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. After installation, a functional test should be performed to confirm that all functions are correct and ensure stable operation of the entire system.
Troubleshooting Steps
-
Preliminary Inspection Process
When troubleshooting a solenoid valve problem, a preliminary inspection is a crucial step. This process typically requires a systematic approach to determine the nature and scope of the problem. First, check the power supply for proper operation. Use a multimeter to measure the power supply voltage to confirm that it is within the rated range for the solenoid valve. If the voltage is lower than the preset value, check the distribution board and switch to ensure proper contact.
Next, check the control circuit connections. Ensure that all terminals are securely connected and free of loose or oxidized components. In some cases, a missing or unstable control signal may cause the solenoid valve to malfunction. Therefore, performing a separate control signal test is necessary, which can be accomplished using a signal generator or the control system's test function.
Check the fluid inlet and outlet to confirm that the fluid is flowing freely. Sometimes, impurities in the fluid can prevent the solenoid valve disc from closing properly or block the valve seat. Disassemble the valve to inspect the internal structure to ensure that no foreign matter or dirt may impair normal operation.
-
Fault Identification Methods
Fault identification should be performed systematically based on the observed symptoms. If the solenoid valve fails to activate, observe its response by pressing the start button or operating the manual switch. If the solenoid valve is sluggish or unresponsive, it may indicate a burnt coil or unstable power supply.
If the valve does not fully open, further check whether the fluid pressure meets the requirements. Low pressure may prevent the valve from fully opening. In this case, use a pressure gauge to measure the pressure to confirm that the actual pressure is within specifications. Conversely, excessive pressure may cause the valve to be physically squeezed and stuck.
Also, pay attention to any unusual noises from the solenoid valve. These noises may indicate problems with internal components. For example, a creaking sound from the coil may indicate an internal short circuit, while a metallic clattering sound from the valve body may indicate wear or misalignment. Recording and analyzing the audio is also an effective method for troubleshooting.
-
Part Replacement
After determining the cause of the problem, select replacement parts according to the manufacturer's guidelines and product manual. If the coil is burnt, use genuine parts that match the original model to avoid quality issues. Also, ensure that the voltage level of the new coil matches the system requirements and that it is securely fastened during installation to prevent loosening. If the valve body needs to be replaced, it's recommended to replace the entire valve assembly rather than just some of the internal components. This is because minor wear and tear inside the valve body can be difficult to detect, and a complete replacement can improve operational safety and stability.
Before replacing any component, record the replacement date and fault details to aid future maintenance and diagnosis. It's also recommended to conduct a quality assessment of the replaced component, especially for parts from non-original suppliers, to verify their performance and durability through testing.
Timely repair and replacement not only extend the life of the solenoid valve but also improve overall system efficiency. Therefore, rapid response and proper handling of faults are crucial to stable factory operations.
Troubleshooting steps include initial inspection, fault identification, and recommended component replacements, all of which are critical to ensuring proper solenoid valve operation. A systematic approach can effectively reduce the likelihood of future failures and ensure the stability and efficiency of the production process.
Looking for professional solenoid valve manufacturers - KUHNWAY
Solenoid valves are crucial components in modern automation control systems, and their operational performance is directly impacting industrial production efficiency and safety. Analysis of various solenoid valve failure cases reveals that the causes often involve electrical or mechanical issues, such as power supply fluctuations, improper installation, or environmental influences. Therefore, establishing a systematic troubleshooting approach, combined with a comprehensive understanding of the operating environment, is crucial for resolving these issues. During troubleshooting, using professional diagnostic tools can more quickly and accurately pinpoint the problem. Furthermore, analyzing the problem from multiple perspectives significantly improves the efficiency and accuracy of fault diagnosis.
Seeking professional technical support is crucial when facing complex or recurring faults. Likai Industrial not only quickly identifies the cause of the fault but also provides optimized recommendations for equipment installation, operation, and maintenance procedures to prevent recurrence.
Solenoid Valve Not Working? 5 Common Malfunctions Explained
KUHNWAY, with over 30 years of solenoid valve manufacturing experience, outlines the 5 most common solenoid valve malfunctions and how to fix them.